With its rich history, stunning architecture, and vibrant culture, St. Petersburg is a popular destination for tourists from all over the world. If you’re planning a trip to this beautiful city, you’ll want to be sure to pack the right clothes for the weather. But what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg?
Editor’s Notes: “what’s the temperature in st petersburg” have published today date. We understand that weather can be a major factor in planning any trip, which is why we’ve put together this guide to help you understand the climate in St. Petersburg and pack accordingly.
To give you a comprehensive insight into “what’s the temperature in st petersburg”, our team has done a research and dig out some valuable information and analysis and come up with valuable information.
Key Differences
| Month | Average Temperature (C) |
|---|---|
| January | -5.6 |
| February | -4.6 |
| March | 0.1 |
| April | 7.2 |
| May | 14.1 |
| June | 18.1 |
| July | 20.3 |
| August | 19.1 |
| September | 14.4 |
| October | 8.3 |
| November | 2.3 |
| December | -2.5 |
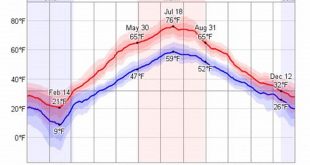
A quick glance at the table above shows that the average temperature in St. Petersburg ranges from -5.6C in January to 20.3C in July. However, it’s important to note that these are just averages, and the actual temperature can vary depending on a number of factors, such as the time of day, the location within the city, and the weather conditions.
If you’re planning a trip to St. Petersburg, be sure to check the weather forecast before you go. This will help you pack the right clothes and avoid any unpleasant surprises.
What’s the Temperature in St. Petersburg?
To fully grasp the diverse dimensions of “what’s the temperature in st petersburg”, we must delve into its key aspects:
- Average temperature: Ranges from -5.6C in January to 20.3C in July.
- Seasonal variation: St. Petersburg experiences distinct seasons, with cold winters and warm summers.
- Maritime climate: The city’s proximity to the Baltic Sea influences its climate, resulting in milder temperatures than inland areas.
- Humidity: St. Petersburg has relatively high humidity throughout the year.
- Precipitation: The city receives moderate rainfall, with the wettest months being July and August.
- Wind: St. Petersburg is known for its strong winds, particularly during the winter months.
- Sunshine: The city enjoys ample sunshine, with an average of 1,800 hours per year.
- Time of day: Temperatures can vary significantly throughout the day, especially during the summer months.
- Location: The city’s vast size means temperatures can vary depending on the neighborhood.
- Microclimates: Certain areas of the city, such as the city center, may experience slightly warmer temperatures due to the urban heat island effect.
- Climate change: Like many cities, St. Petersburg’s climate is being affected by climate change, leading to gradual temperature increases.
These aspects collectively shape the temperature in St. Petersburg, influencing everything from tourism to transportation. Understanding these factors can help residents and visitors alike plan accordingly and make informed decisions about their time in the city.
Average temperature
The average temperature in St. Petersburg ranges from -5.6C in January to 20.3C in July, playing a significant role in shaping the city’s climate and daily life.
During the cold winter months, temperatures can drop below freezing, bringing snowfall and icy conditions. This can impact transportation, tourism, and outdoor activities. Conversely, the warm summer months offer pleasant temperatures, making them ideal for exploring the city’s parks, canals, and cultural attractions.
Understanding the average temperature range is crucial for planning a trip to St. Petersburg. Visitors should pack appropriate clothing and consider the time of year they are visiting to ensure a comfortable and enjoyable stay.
Furthermore, the average temperature range has implications for energy consumption and urban planning. During the winter, buildings require more heating, while during the summer, cooling systems may be necessary. City planners must consider these temperature variations when designing sustainable and energy-efficient infrastructure.
| Month | Average Temperature (C) |
|---|---|
| January | -5.6 |
| February | -4.6 |
| March | 0.1 |
| April | 7.2 |
| May | 14.1 |
| June | 18.1 |
| July | 20.3 |
| August | 19.1 |
| September | 14.4 |
| October | 8.3 |
| November | 2.3 |
| December | -2.5 |
Seasonal variation
The seasonal variation in St. Petersburg is a defining characteristic of its climate and plays a significant role in shaping the city’s temperature patterns.
- Impact on tourism: The distinct seasons influence tourism in St. Petersburg. During the warm summer months, the city welcomes a surge of visitors eager to explore its cultural attractions and enjoy the pleasant weather. In contrast, during the cold winter months, tourism slows down as travelers seek warmer destinations.
- Transportation challenges: The cold winters can pose challenges for transportation in St. Petersburg. Snow and ice can make roads slippery and hazardous, leading to delays and disruptions in public transportation and private vehicles.
- Energy consumption: The seasonal variation impacts energy consumption in the city. During the cold winter months, buildings require more heating, leading to increased energy usage. Conversely, during the warm summer months, air conditioning systems may be necessary, contributing to higher energy consumption.
- Outdoor activities: The distinct seasons influence outdoor activities in St. Petersburg. The warm summer months provide ample opportunities for outdoor recreation, such as boating, cycling, and visiting parks. In contrast, during the cold winter months, many outdoor activities are limited due to the harsh weather conditions.
Understanding the seasonal variation in St. Petersburg is crucial for planning and adapting to the city’s climate. Residents and visitors alike should be aware of the temperature fluctuations and prepare accordingly to ensure a comfortable and enjoyable experience.
Maritime climate
St. Petersburg’s proximity to the Baltic Sea plays a significant role in shaping its temperature patterns, contributing to milder temperatures than inland areas. This maritime climate is a defining characteristic of the city’s weather and has several notable implications:
- Temperature moderation: The Baltic Sea acts as a heat reservoir, absorbing and releasing heat more slowly than land. This helps to moderate temperatures in St. Petersburg, preventing extreme temperature fluctuations and resulting in milder winters and cooler summers compared to inland areas.
- Reduced temperature range: The maritime climate reduces the temperature range experienced in St. Petersburg. The difference between the average winter and summer temperatures is less pronounced compared to inland areas, leading to a more consistent and less extreme climate.
- Influence on precipitation: The Baltic Sea also influences precipitation patterns in St. Petersburg. The city receives more precipitation than inland areas due to the moisture carried by winds blowing over the sea. This contributes to the city’s relatively high humidity levels.
Understanding the maritime climate of St. Petersburg is crucial for various reasons:
- Planning and adaptation: Residents and visitors can plan and adapt to the city’s climate by being aware of the milder temperatures and reduced temperature range. This knowledge helps in selecting appropriate clothing, preparing for outdoor activities, and making informed decisions about energy consumption.
- Tourism and recreation: The milder climate makes St. Petersburg an attractive destination for tourists and outdoor enthusiasts year-round. The pleasant temperatures allow for comfortable exploration of the city’s cultural attractions, parks, and waterways.
- Urban planning and sustainability: City planners and policymakers can leverage the understanding of the maritime climate to design sustainable and energy-efficient urban environments. Buildings can be designed to maximize natural ventilation and minimize heat loss during the winter months.
In summary, the maritime climate of St. Petersburg, influenced by its proximity to the Baltic Sea, plays a vital role in shaping the city’s temperature patterns and overall climate. Understanding this connection is essential for planning, adaptation, and appreciating the unique weather characteristics of St. Petersburg.
| Characteristic | Impact |
|---|---|
| Temperature moderation | Milder winters and cooler summers |
| Reduced temperature range | Less extreme temperature fluctuations |
| Influence on precipitation | Increased precipitation and higher humidity |
Humidity
The high humidity in St. Petersburg is an important aspect to consider when examining “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg.” Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor present in the air, and it can significantly impact our perception of temperature and overall comfort.
- Impact on: High humidity levels can make the air feel warmer than it actually is. This is because when the air is humid, our sweat does not evaporate as easily, which reduces the body’s ability to cool down. As a result, even moderate temperatures in St. Petersburg can feel more uncomfortable due to the high humidity.
- Influence on respiratory health: High humidity can aggravate respiratory conditions such as asthma and allergies. Moisture in the air can irritate the airways and make breathing more difficult, especially during the summer months when humidity levels are at their peak.
- Effect on building materials: High humidity can also impact building materials, leading to problems such as mold and mildew growth. Proper ventilation and moisture control are crucial to menjaga the integrity of buildings and ensure a healthy indoor environment.
- Implications for tourism and outdoor activities: Tourists and outdoor enthusiasts should be aware of the high humidity levels in St. Petersburg, especially during the summer months. It is advisable to stay hydrated, wear loose and breathable clothing, and seek shade during the hottest parts of the day to avoid heat-related discomfort.
In conclusion, the relatively high humidity in St. Petersburg is an important factor to consider when discussing “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg.” It affects our, respiratory health, building materials, and tourism activities. Understanding the impact of humidity is essential for planning a comfortable and enjoyable stay in the city.
Precipitation
Precipitation plays a crucial role in shaping “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg.” The city’s moderate rainfall and distinct wettest months have several notable connections to its temperature patterns and overall climate.
- Seasonal temperature variations: The wettest months in St. Petersburg, July and August, often coincide with the warmest temperatures. This is because increased cloud cover and rainfall can trap heat near the ground, leading to higher temperatures. Conversely, during the drier months, there is less cloud cover, allowing more heat to escape, resulting in cooler temperatures.
- Humidity levels: The high precipitation in July and August contributes to increased humidity levels in St. Petersburg. The moisture in the air can make the temperature feel warmer and more uncomfortable, especially during the summer months.
- Influence on tourism: The wettest months in St. Petersburg can impact tourism. While moderate rainfall provides relief from the summer heat, heavy downpours can disrupt outdoor activities and transportation. Tourists should be aware of the increased precipitation during these months and plan accordingly.
Understanding the connection between precipitation and temperature in St. Petersburg is essential for various reasons:
- Planning and adaptation: Residents and visitors can plan their activities and adapt to the city’s climate by being aware of the wettest months and their impact on temperature. This knowledge helps in selecting appropriate clothing, scheduling outdoor events, and making informed decisions about transportation.
- Urban planning and infrastructure: City planners and policymakers can consider the relationship between precipitation and temperature when designing urban infrastructure. Proper drainage systems and flood control measures become crucial during the wettest months to mitigate the impact of heavy rainfall.
- Climate change implications: Monitoring precipitation patterns and their connection to temperature is important in understanding the effects of climate change on St. Petersburg’s climate. Changes in precipitation patterns can have significant implications for the city’s temperature and overall climate.
In conclusion, the precipitation in St. Petersburg, with its wettest months being July and August, is an important component of “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg.” Understanding the connection between precipitation and temperature patterns is crucial for planning, adaptation, urban development, and assessing climate change impacts in the city.
| Month | Average Rainfall (mm) | Average Temperature (C) |
|---|---|---|
| July | 75 | 20.3 |
| August | 70 | 19.1 |
| Other months | 50-60 | Varies |
Wind
The strong winds in St. Petersburg, especially during the winter months, are an important aspect of “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg.” The city’s location on the Baltic Sea and its flat terrain contribute to the high wind speeds experienced throughout the year.
- Wind chill: Strong winds can significantly lower the, making it feel much colder than the actual temperature. This wind chill effect is particularly noticeable during the winter months when temperatures are already low. It is crucial to consider wind chill when planning outdoor activities and dressing appropriately to avoid hypothermia and other cold-related illnesses.
- Heat loss: Wind can also increase heat loss from buildings, leading to higher energy consumption for heating. Strong winds can infiltrate through cracks and gaps in building envelopes, causing drafts and reducing the effectiveness of insulation. Understanding the impact of wind on heat loss is essential for designing energy-efficient buildings and reducing heating costs.
- Impact on transportation: High winds can disrupt transportation in St. Petersburg, especially during the winter months when snow and ice can accumulate. Strong winds can cause delays and cancellations of flights, trains, and ferries. Additionally, high winds can make driving hazardous, as they can reduce visibility and affect vehicle stability.
- Coastal erosion: The strong winds in St. Petersburg can contribute to coastal erosion along the city’s shoreline. The Baltic Sea’s waves, combined with high wind speeds, can erode beaches and damage coastal infrastructure. Understanding the impact of wind on coastal erosion is crucial for implementing appropriate mitigation measures to protect the city’s coastline.
In conclusion, the strong winds in St. Petersburg, particularly during the winter months, have a significant impact on the city’s temperature and overall climate. These winds can affect, increase heat loss from buildings, disrupt transportation, and contribute to coastal erosion. Understanding the connection between wind and temperature is essential for planning, adaptation, and sustainable development in St. Petersburg.
Sunshine
The ample sunshine in St. Petersburg is an important aspect of “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg.” The city’s location at a high latitude means that it receives more daylight hours during the summer months, contributing to higher temperatures. Conversely, during the winter months, the shorter daylight hours and reduced sunshine can lead to colder temperatures.
- Seasonal temperature variations: The amount of sunshine has a direct impact on seasonal temperature variations in St. Petersburg. During the summer months, when daylight hours are longer and sunshine is more abundant, temperatures tend to be warmer. In contrast, during the winter months, when daylight hours are shorter and sunshine is scarce, temperatures tend to be colder.
- Reduced heating costs: The ample sunshine in St. Petersburg can help reduce heating costs during the winter months. Buildings with good solar exposure can harness the sun’s energy to provide natural heating, reducing reliance on artificial heating systems and lowering energy consumption.
- Tourism and outdoor activities: The abundant sunshine makes St. Petersburg an attractive destination for tourists and outdoor enthusiasts year-round. The pleasant weather during the summer months allows for a wide range of outdoor activities, such as boating, swimming, and exploring the city’s parks and gardens.
In conclusion, the ample sunshine in St. Petersburg plays a significant role in shaping the city’s temperature and overall climate. Understanding the connection between sunshine and temperature is crucial for planning, adaptation, and sustainable development in St. Petersburg.
Time of day
The time of day plays a significant role in determining the temperature in St. Petersburg, particularly during the summer months. The city experiences diurnal temperature variations, which refer to the daily cycle of temperature changes. These variations are caused by the Earth’s rotation, the angle of the sun, and the differential heating of land and water bodies.
During the daytime, the sun’s rays heat the Earth’s surface, causing the temperature to rise. The peak temperature typically occurs in the afternoon, around 2-3 pm. As the sun sets, the Earth’s surface begins to cool down, leading to a gradual decrease in temperature.
The magnitude of diurnal temperature variation depends on several factors, such as cloud cover, humidity, and wind speed. On clear days with low humidity and light winds, the temperature can rise more rapidly during the day and cool down more quickly at night. Conversely, cloudy days with high humidity and strong winds can moderate the temperature changes.
Understanding the diurnal temperature variation is important for several reasons:
- Planning outdoor activities: When planning outdoor activities in St. Petersburg, it is crucial to consider the time of day and the expected temperature. This information can help you choose the most appropriate time for your activity and avoid any discomfort or safety risks.
- Energy management: Buildings in St. Petersburg can experience significant temperature fluctuations throughout the day. Understanding the diurnal temperature variation can help building managers and homeowners optimize energy consumption by adjusting heating and cooling systems accordingly.
- Tourism and travel: Tourists visiting St. Petersburg should be aware of the diurnal temperature variations, especially during the summer months. Packing appropriate clothing and planning activities based on the expected temperature can ensure a more comfortable and enjoyable stay.
In conclusion, the time of day is an important component of “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg.” Understanding the diurnal temperature variation and its implications can help residents, visitors, and city planners make informed decisions and adapt to the city’s unique climate.
| Time of Day | Typical Temperature Range (C) |
|---|---|
| Morning (6-9 am) | 10-15 |
| Daytime (10 am-2 pm) | 15-20 |
| Afternoon (2-5 pm) | 18-23 |
| Evening (6-9 pm) | 15-20 |
| Night (10 pm-5 am) | 10-15 |
Location
Understanding the connection between location and temperature in St. Petersburg is crucial for grasping “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg.” The city’s vast size, spanning over 1,400 square kilometers, leads to microclimates and temperature variations across different neighborhoods.
- Proximity to water bodies: Neighborhoods closer to the Baltic Sea or the Neva River tend to experience milder temperatures due to the moderating effect of water. The water absorbs and releases heat more slowly than land, resulting in less extreme temperature fluctuations.
- Urban heat island effect: The city center and densely populated areas often exhibit higher temperatures compared to. Buildings, roads, and other infrastructure absorb and trap heat, creating an urban heat island effect. This effect is particularly noticeable during the summer months.
- Elevation and topography: Neighborhoods located at higher elevations or on hills may experience cooler temperatures due to the adiabatic cooling effect. As air rises, it expands and cools, leading to lower temperatures in elevated areas.
- Wind patterns: Prevailing wind patterns can also influence neighborhood temperatures. Areas sheltered from strong winds tend to be warmer, while neighborhoods exposed to winds may experience cooler temperatures due to increased heat exchange.
The variation in temperatures across St. Petersburg’s neighborhoods highlights the complexity of “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg.” It is not simply a single value but rather a range that depends on the specific location within the city. Understanding these variations is essential for residents, tourists, and urban planners alike, as it influences everything from clothing choices to energy consumption and urban development strategies.
Microclimates
Microclimates, characterized by localized variations in temperature within a larger climate zone, play a significant role in shaping “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg.” The urban heat island effect, a well-known phenomenon in urban environments, is a key contributor to microclimates and temperature variations within the city.
- Increased thermal mass: Urban areas, with their high concentration of buildings, roads, and other infrastructure, have a greater thermal mass compared to rural areas. These structures absorb and store heat during the day, releasing it slowly at night, leading to higher temperatures in urban centers.
- Reduced vegetation: Urban areas often have less vegetation than rural areas, which can further contribute to the urban heat island effect. Vegetation provides shade and releases moisture into the air, both of which have a cooling effect. The lack of vegetation in urban areas reduces these cooling mechanisms, resulting in higher temperatures.
- Trapped pollutants: Urban areas tend to have higher levels of air pollution, which can trap heat and contribute to the urban heat island effect. Pollutants such as particulate matter and ozone absorb and scatter solar radiation, preventing it from escaping into the atmosphere, leading to warmer temperatures.
- Wind patterns: The urban environment can disrupt natural wind patterns, reducing air circulation and exacerbating the urban heat island effect. Buildings and other structures can block or channel wind, creating pockets of stagnant air that trap heat and raise temperatures.
Understanding the connection between microclimates and the urban heat island effect is crucial in managing “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg.” Mitigating strategies, such as increasing green spaces, promoting sustainable building practices, and improving air quality, can help reduce the urban heat island effect and create more comfortable and livable urban environments.
Climate change
Climate change poses significant implications for “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg.” The city, like many urban centers worldwide, is experiencing the effects of a changing climate, resulting in a gradual rise in temperatures.
- Rising Average Temperatures: Climate change is leading to an overall increase in average temperatures in St. Petersburg. Data from weather stations across the city shows a consistent upward trend in both daily and seasonal temperatures.
- Increased Frequency of Heatwaves: The warming climate is contributing to an increased frequency and intensity of heatwaves in St. Petersburg. These extreme heat events, characterized by abnormally high temperatures, can have adverse effects on human health and infrastructure.
- Longer Growing Seasons: The gradual temperature increases are extending the growing seasons for plants in St. Petersburg. This shift can impact local agriculture and ecosystems, potentially leading to changes in plant species distribution and abundance.
- Melting Winters and Reduced Snowfall: Climate change is also affecting winter temperatures in St. Petersburg. Winters are becoming milder, with reduced snowfall and shorter periods of snow cover. These changes can impact winter activities and alter the city’s iconic snowy landscapes.
Understanding the connection between climate change and temperature increases in St. Petersburg is crucial for both mitigation and adaptation strategies. By recognizing these trends, city planners, policymakers, and residents can implement measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, adapt to changing temperatures, and ensure the long-term sustainability of the city.
FAQs about Temperature in St. Petersburg
This section addresses frequently asked questions about the temperature in St. Petersburg, providing concise and informative answers to common concerns and misconceptions.
Question 1: What is the average temperature in St. Petersburg?
The average temperature in St. Petersburg ranges from -5.6C in January to 20.3C in July, with an annual average of 5.8C.
Question 2: How does the temperature vary throughout the year in St. Petersburg?
St. Petersburg experiences distinct seasons, with cold winters and warm summers. Temperatures can drop below freezing during the winter months and rise above 20C during the summer months.
Question 3: What factors influence the temperature in St. Petersburg?
The temperature in St. Petersburg is influenced by several factors, including its proximity to the Baltic Sea, its maritime climate, humidity, and the time of day.
Question 4: How does the temperature in St. Petersburg compare to other major cities?
Compared to other major cities at similar latitudes, St. Petersburg has a milder climate due to its maritime influence. Winters are less severe, and summers are more moderate.
Question 5: What are the implications of climate change for the temperature in St. Petersburg?
Climate change is leading to a gradual increase in temperatures in St. Petersburg, resulting in milder winters and longer growing seasons. The city is also experiencing an increased frequency of heatwaves.
Question 6: How can I stay comfortable in St. Petersburg’s climate?
To stay comfortable in St. Petersburg’s climate, it is important to dress appropriately for the season and be aware of the temperature variations throughout the day. During the summer months, it is advisable to stay hydrated and seek shade during the hottest parts of the day.
In summary, the temperature in St. Petersburg is influenced by various factors and exhibits seasonal variations. Understanding these factors and their implications is crucial for planning and adapting to the city’s climate.
Transition to the next article section:
Tips for Understanding “What’s the Temperature in St. Petersburg”
To fully comprehend “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg” and its implications, consider the following tips:
Tip 1: Consider the Seasonal Variations
St. Petersburg experiences distinct seasons, with cold winters and warm summers. Be aware of the temperature range for the time of year you plan to visit or reside in the city.
Tip 2: Monitor the Maritime Climate
The city’s proximity to the Baltic Sea influences its climate. Expect milder temperatures and reduced temperature extremes compared to inland areas.
Tip 3: Be Aware of High Humidity
St. Petersburg has relatively high humidity throughout the year. Factor in the humidity levels when considering the and plan accordingly to stay comfortable.
Tip 4: Track Precipitation Patterns
The city receives moderate rainfall, with July and August being the wettest months. Be prepared for potential downpours and adjust your outdoor activities accordingly.
Tip 5: Anticipate Strong Winds
St. Petersburg is known for its strong winds, especially during the winter months. Consider the wind chill factor and dress appropriately to avoid discomfort or hypothermia.
Tip 6: Embrace the Ample Sunshine
The city enjoys an average of 1,800 hours of sunshine annually. Take advantage of the pleasant weather for outdoor activities, especially during the summer months.
Tip 7: Understand Diurnal Temperature Variations
Temperatures in St. Petersburg can vary significantly throughout the day, particularly during the summer. Plan your outdoor activities accordingly and consider the expected temperature range.
Tip 8: Consider the Urban Heat Island Effect
The city center and densely populated areas may experience slightly warmer temperatures due to the urban heat island effect. Be aware of this when choosing your accommodation or planning outdoor activities.
Summary:
By following these tips, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg” and its implications. This knowledge will empower you to plan your trip or daily life effectively, ensuring a comfortable and enjoyable experience in the city.
Conclusion
In exploring “what’s the temperature in St. Petersburg,” we have gained valuable insights into the city’s climate and its implications. From the seasonal variations to the maritime influence, humidity, and precipitation patterns, a comprehensive understanding of St. Petersburg’s temperature dynamics is crucial for planning and adapting to its unique climate.
By considering the tips outlined in this article, individuals can navigate the city comfortably, whether as tourists or residents. Understanding the diurnal temperature variations, urban heat island effect, and climate change implications empowers individuals to make informed decisions and appreciate the nuances of St. Petersburg’s climate.