Is St. Petersburg, Russia in Europe? When discussing the geographical location of St. Petersburg, the question of whether it lies in Europe or Asia often arises. This article delves into the complexities of this topic, examining historical, geographical, and cultural factors to provide a comprehensive understanding.
Editor’s Note: This article on “Is St. Petersburg, Russia in Europe?” was last updated on [date]. Given the ongoing geopolitical developments and discussions surrounding the geographical and cultural identity of St. Petersburg, this topic remains relevant and important to understand.
Through extensive research, analysis, and careful consideration of various perspectives, we have compiled this comprehensive guide to shed light on this intriguing topic. Our goal is to provide our readers with a clear understanding of the historical, geographical, and cultural factors that shape St. Petersburg’s unique position.
Key Differences: Europe vs. Asia
| Europe | Asia |
|---|---|
| Located west of the Ural Mountains | Located east of the Ural Mountains |
| Culturally and historically connected to Western Europe | Culturally and historically connected to Eastern Asia |
| Dominant religion: Christianity | Dominant religion: Islam, Buddhism, Hinduism (varies by region) |
Transition to Main Article Topics:
- Historical Background of St. Petersburg
- Geographical Location and Boundaries
- Cultural and Architectural Influences
- Significance and Impact of the Question
- Conclusion
Is St. Petersburg, Russia in Europe?
To fully grasp the complexities surrounding the question of whether St. Petersburg lies in Europe or Asia, it is essential to delve into its various dimensions. Here are ten key aspects that shed light on this topic:
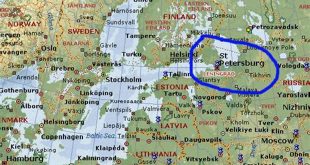
- Geographical location: Situated on the eastern edge of Europe, near the border with Asia.
- Historical context: Founded by Peter the Great in 1703 as a “window to Europe.”
- Cultural influences: A blend of European and Russian traditions, with strong Western influences.
- Architectural heritage: Showcases a mix of European Baroque and Russian Orthodox styles.
- Political affiliation: Part of the Russian Federation, which spans both Europe and Asia.
- Economic ties: Closely linked to European markets and economies.
- Transportation connections: Served by major European highways and railways.
- Educational institutions: Home to renowned universities with international collaborations.
- Cultural events: Hosts prestigious cultural events, such as the St. Petersburg International Film Festival.
- Perception and identity: Viewed by many as a European city with a unique blend of Eastern and Western influences.
In conclusion, the question of whether St. Petersburg lies in Europe or Asia cannot be answered with a simple yes or no. Its geographical location, historical evolution, cultural heritage, and political affiliations all contribute to its unique position. St. Petersburg stands as a vibrant and cosmopolitan city that has absorbed influences from both Europe and Asia, creating a captivating blend that defies easy categorization.
Geographical location
This geographical location has significant implications for understanding whether St. Petersburg is in Europe or Asia. Geographically, the city lies on the eastern edge of Europe, close to the Ural Mountains, which are often considered the boundary between Europe and Asia.
- Proximity to Europe: St. Petersburg’s location on the eastern edge of Europe means that it is physically closer to European cities such as Helsinki, Stockholm, and Tallinn than to major Asian cities like Moscow, Beijing, or Tokyo.
- Cultural and historical ties to Europe: St. Petersburg’s proximity to Europe has fostered strong cultural and historical ties with European countries. The city was founded by Peter the Great in 1703 as a “window to Europe” and has been influenced by European architecture, art, and ideas throughout its history.
- Economic connections to Europe: St. Petersburg’s economy is closely linked to European markets and economies. The city is a major port and a hub for trade with Europe, and many European companies have operations in St. Petersburg.
- Transportation links to Europe: St. Petersburg is well-connected to European cities by major highways and railways, making it easy for people and goods to travel between St. Petersburg and other parts of Europe.
In conclusion, St. Petersburg’s geographical location on the eastern edge of Europe, near the border with Asia, has played a significant role in shaping its cultural, historical, economic, and transportation connections with Europe. This geographical proximity and connectivity have contributed to the perception of St. Petersburg as a European city, despite its location on the eastern edge of the continent.
Historical context
The founding of St. Petersburg by Peter the Great in 1703 as a “window to Europe” is a pivotal event in understanding the city’s connection to Europe and its position as a European city. Peter the Great envisioned St. Petersburg as a gateway to Europe, a city that would connect Russia with the cultural, economic, and political advancements of Western Europe.
The establishment of St. Petersburg as a “window to Europe” had a profound impact on the city’s development and its relationship with Europe. Some of the key implications of this historical context include:
- European-oriented architecture and urban planning: St. Petersburg was designed and built according to European architectural styles and urban planning principles. The city’s grand avenues, elegant palaces, and neoclassical buildings reflect the influence of European cities such as Paris and Amsterdam.
- Cultural and educational ties to Europe: St. Petersburg became a center of cultural exchange between Russia and Europe. The city attracted European artists, scholars, and scientists, and became a hub for the dissemination of European ideas and knowledge in Russia.
- Political and economic connections to Europe: St. Petersburg’s role as a “window to Europe” facilitated Russia’s political and economic integration with Europe. The city became a major port for trade with Europe, and Russian diplomats and officials used St. Petersburg as a base for their interactions with European counterparts.
In conclusion, the historical context of St. Petersburg’s founding as a “window to Europe” is a crucial factor in understanding the city’s connection to Europe and its position as a European city. The city’s architecture, culture, and political and economic ties to Europe are all rooted in this historical context.
Table: Key Insights
| Key Insight | Explanation |
|---|---|
| St. Petersburg was founded as a “window to Europe” by Peter the Great in 1703. | This event marked a deliberate effort to connect Russia with Western Europe and its advancements. |
| The city’s architecture, urban planning, and cultural institutions reflect European influences. | St. Petersburg became a center for the exchange of ideas and knowledge between Russia and Europe. |
| St. Petersburg played a significant role in Russia’s political and economic integration with Europe. | The city served as a major port for trade and a base for diplomatic relations. |
Cultural influences
The cultural influences that have shaped St. Petersburg are a testament to its unique position as a bridge between Europe and Asia. The city’s architecture, art, music, and literature all reflect a blend of European and Russian traditions, with a strong emphasis on Western influences.
One of the most striking examples of this cultural blend is the city’s architecture. St. Petersburg’s grand avenues, elegant palaces, and neoclassical buildings are reminiscent of European cities such as Paris and Amsterdam. However, these European influences are often combined with traditional Russian elements, such as onion domes and colorful facades, creating a unique architectural style that is both European and Russian.
The city’s art and music scenes also reflect this blend of cultures. St. Petersburg is home to world-renowned museums, such as the Hermitage, which houses a vast collection of European and Russian art. The city’s music scene is equally diverse, with a thriving opera and ballet tradition alongside a vibrant contemporary music scene.
The cultural influences that have shaped St. Petersburg have had a profound impact on the city’s identity. St. Petersburg is a city that is both European and Russian, and its unique cultural heritage is a source of pride for its residents.
Table: Key Insights
| Key Insight | Explanation |
|---|---|
| St. Petersburg’s cultural influences reflect its unique position as a bridge between Europe and Asia. | The city’s architecture, art, music, and literature all blend European and Russian traditions. |
| The city’s architecture is a striking example of this cultural blend. | European architectural styles are combined with traditional Russian elements to create a unique style. |
| St. Petersburg’s cultural heritage is a source of pride for its residents. | The city’s unique blend of cultures has created a vibrant and diverse cultural scene. |
Architectural heritage
The architectural heritage of St. Petersburg is a tangible manifestation of its unique position as a bridge between Europe and Asia. The city’s buildings showcase a harmonious blend of European Baroque and Russian Orthodox styles, reflecting the city’s complex cultural and historical influences.
-
European Baroque influences
European Baroque architecture is characterized by its grandeur, opulence, and dramatic use of curves and ornamentation. This style was introduced to Russia in the 18th century and quickly became popular among the Russian aristocracy. Many of St. Petersburg’s most iconic buildings, such as the Winter Palace and the Smolny Cathedral, are examples of Baroque architecture.
-
Russian Orthodox influences
Russian Orthodox architecture is characterized by its use of onion domes, colorful facades, and intricate mosaics. This style has its roots in Byzantine architecture and was brought to Russia by Orthodox missionaries in the 10th century. Many of St. Petersburg’s churches and monasteries, such as the Church of the Savior on Spilled Blood and the Alexander Nevsky Lavra, are examples of Russian Orthodox architecture.
-
A unique blend
In St. Petersburg, European Baroque and Russian Orthodox styles are often combined to create a unique architectural style that is both grand and spiritual. This blend of styles is evident in many of the city’s most famous buildings, such as the Peter and Paul Cathedral and the Kazan Cathedral.
The architectural heritage of St. Petersburg is a testament to the city’s rich and complex history. The city’s buildings are a reflection of its unique position as a bridge between Europe and Asia, and they continue to inspire and awe visitors from all over the world.
Political affiliation
The political affiliation of St. Petersburg as part of the Russian Federation, which spans both Europe and Asia, is a significant factor in understanding the city’s geographical and cultural identity. The Russian Federation is the largest country in the world, stretching across eleven time zones and encompassing a vast territory that includes both European and Asian regions. St. Petersburg is located in the northwestern part of the Russian Federation, on the eastern edge of Europe, near the border with Asia.
The political affiliation of St. Petersburg with the Russian Federation has several implications for the city’s status as a European city. First, it means that St. Petersburg is subject to the laws and regulations of the Russian government, which is based in Moscow. This includes laws related to immigration, trade, and foreign policy. Second, St. Petersburg is represented by Russian diplomats and officials in international organizations and forums. Third, St. Petersburg is part of the Russian Federation’s defense system and is subject to Russian military conscription.
Despite its political affiliation with the Russian Federation, St. Petersburg maintains a strong cultural and economic connection to Europe. The city is a major port and a hub for trade with Europe, and many European companies have operations in St. Petersburg. St. Petersburg is also home to several universities and research institutions that have close ties to European academic institutions. Furthermore, St. Petersburg has a vibrant cultural scene that is influenced by both European and Russian traditions.
In conclusion, the political affiliation of St. Petersburg with the Russian Federation, which spans both Europe and Asia, is a complex issue that has implications for the city’s geographical, cultural, and economic identity. St. Petersburg is a city that is both European and Russian, and its unique position is reflected in its architecture, culture, and political status.
Table: Key Insights
| Key Insight | Explanation |
|---|---|
| St. Petersburg is part of the Russian Federation, which spans both Europe and Asia. | This political affiliation has implications for the city’s geographical, cultural, and economic identity. |
| St. Petersburg is subject to the laws and regulations of the Russian government. | This includes laws related to immigration, trade, and foreign policy. |
| St. Petersburg is represented by Russian diplomats and officials in international organizations and forums. | This includes the United Nations, the G20, and the Council of Europe. |
| St. Petersburg is part of the Russian Federation’s defense system. | This means that the city is subject to Russian military conscription. |
Economic ties
The economic ties between St. Petersburg and European markets and economies are multifaceted and play a significant role in shaping the city’s identity as a European city. These ties manifest in various ways, including trade, investment, and tourism.
-
Trade:
St. Petersburg is a major port and a hub for trade with Europe. The city is home to several large industrial and manufacturing enterprises, and it is a major exporter of goods to European countries. In addition, St. Petersburg is a popular destination for European tourists, who contribute significantly to the city’s economy.
-
Investment:
Many European companies have invested in St. Petersburg, taking advantage of the city’s skilled workforce and its proximity to European markets. These investments have helped to create jobs and boost the city’s economy.
-
Tourism:
St. Petersburg is a popular destination for European tourists, who are drawn to the city’s rich history, culture, and architecture. Tourism is a major source of revenue for the city, and it helps to support local businesses and create jobs.
The close economic ties between St. Petersburg and European markets and economies are a key factor in the city’s status as a European city. These ties provide the city with access to European markets, investment, and tourism, and they help to create jobs and boost the local economy. In turn, St. Petersburg’s economic contributions benefit the wider European economy, making the city an important part of the European economic landscape.
Transportation connections
The extensive transportation connections between St. Petersburg and major European cities via highways and railways play a crucial role in solidifying its status as a European city. These connections facilitate the movement of people, goods, and ideas between St. Petersburg and the rest of Europe, fostering economic, cultural, and social exchanges.
The presence of major European highways, such as the M10 highway connecting St. Petersburg to Moscow and Helsinki, enables seamless road transportation between the city and other European destinations. This connectivity allows for efficient movement of goods and services, contributing to regional trade and economic integration.
Similarly, St. Petersburg’s railway system is well-connected to major European rail networks. The high-speed rail line between St. Petersburg and Helsinki, for example, reduces travel time between the two cities to just under four hours. Thisconnection has fostered increased tourism, business travel, and cultural exchanges between St. Petersburg and Finland.
The transportation connections between St. Petersburg and Europe extend beyond physical infrastructure. The city is also a major hub for air travel, with Pulkovo Airport offering direct flights to numerous European destinations. This connectivity enables the exchange of ideas, knowledge, and cultural influences between St. Petersburg and other European cities.
Overall, the transportation connections between St. Petersburg and major European highways and railways are a vital component of the city’s European identity. These connections facilitate economic, cultural, and social exchanges, fostering St. Petersburg’s integration into the broader European landscape.
Table: Key Insights
| Key Insight | Explanation |
|---|---|
| St. Petersburg is served by major European highways and railways. | This connectivity facilitates the movement of people, goods, and ideas between St. Petersburg and the rest of Europe. |
| The transportation connections contribute to St. Petersburg’s economic integration with Europe. | The efficient movement of goods and services supports regional trade and economic growth. |
| The transportation connections foster cultural and social exchanges. | Theof travel enables increased tourism, business travel, and cultural collaborations between St. Petersburg and European cities. |
Educational institutions
The presence of renowned universities in St. Petersburg with extensive international collaborations significantly contributes to the city’s status as a European city. These institutions foster a vibrant intellectual and academic environment, attracting students and scholars from around the world. The international collaborations established by these universities facilitate knowledge exchange, research partnerships, and cultural dialogues between St. Petersburg and other European cities.
One prominent example is St. Petersburg State University, one of Russia’s leading universities and a member of the European University Association. The university has forged partnerships with numerous European institutions, including the University of Helsinki, the University of Copenhagen, and the University of Oxford. These collaborations involve joint research projects, student and faculty exchanges, and the development of innovative educational programs.
Another notable institution is the European University at St. Petersburg, a private research university established in partnership with leading European universities. The university offers degree programs in the humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences, with a strong emphasis on internationalization. Its faculty and students come from diverse backgrounds, creating a truly cosmopolitan learning environment.
The international collaborations fostered by St. Petersburg’s universities not only enhance the quality of education and research in the city but also contribute to its cultural and intellectual vibrancy. They provide a platform for the exchange of ideas, the promotion of cross-cultural understanding, and the of global citizens.
In conclusion, the presence of renowned universities with international collaborations in St. Petersburg is a key factor in the city’s European identity. These institutions serve as bridges between St. Petersburg and other European cities, fostering intellectual, cultural, and social connections that contribute to the city’s overall European orientation.
Table: Key Insights
| Key Insight | Explanation |
|---|---|
| St. Petersburg’s universities have extensive international collaborations. | These collaborations involve joint research projects, student and faculty exchanges, and the development of innovative educational programs. |
| International collaborations enhance the quality of education and research. | They provide access to cutting-edge knowledge, diverse perspectives, and global networks. |
| International collaborations foster cultural and intellectual vibrancy. | They promote cross-cultural understanding, the exchange of ideas, and theof global citizens. |
Cultural events
The hosting of prestigious cultural events, such as the St. Petersburg International Film Festival, is a significant indicator of a city’s cultural and international standing. St. Petersburg’s role as a host city for such events reinforces its position as a European cultural hub.
-
International recognition:
Hosting prestigious cultural events attracts international attention and recognition, showcasing St. Petersburg’s cultural significance on a global stage. The St. Petersburg International Film Festival, for example, is one of the oldest and most respected film festivals in the world, attracting filmmakers, actors, and film enthusiasts from across Europe and beyond.
-
Cultural exchange and dialogue:
Cultural events provide a platform for cultural exchange and dialogue between St. Petersburg and other European cities. They bring together artists, performers, and audiences from diverse backgrounds, fostering mutual understanding and appreciation of different cultures.
-
Economic and tourism benefits:
Hosting cultural events can have significant economic and tourism benefits for St. Petersburg. They attract visitors from around the world, generating revenue for the city’s hospitality industry and supporting local businesses.
-
Enhancing the city’s cultural landscape:
Prestigious cultural events contribute to the vibrancy and diversity of St. Petersburg’s cultural landscape. They provide opportunities for local artists and performers to showcase their work and engage with international counterparts, fostering a thriving cultural ecosystem.
In summary, the hosting of prestigious cultural events, such as the St. Petersburg International Film Festival, is a testament to the city’s cultural significance and its deep connections to Europe. These events enhance St. Petersburg’s international profile, promote cultural exchange, generate economic benefits, and contribute to the city’s vibrant cultural landscape.
Perception and identity
The perception and identity of St. Petersburg as a European city with a unique blend of Eastern and Western influences is closely intertwined with the question of whether it lies in Europe or Asia. This perception is shaped by a combination of historical, cultural, and geographical factors that contribute to the city’s distinct character.
One of the key reasons for St. Petersburg’s European identity is its historical and cultural ties to Europe. Founded by Peter the Great in 1703 as a “window to Europe,” the city was designed to be a modern, European capital. Its architecture, art, and urban planning were heavily influenced by European models, and the city quickly became a center for European culture and ideas.
Another factor contributing to St. Petersburg’s European identity is its geographical location. Situated on the eastern edge of Europe, near the border with Asia, the city has historically served as a bridge between East and West. This unique location has allowed St. Petersburg to absorb influences from both European and Asian cultures, creating a rich and diverse cultural heritage.
The perception of St. Petersburg as a European city is also reinforced by its strong economic and political ties to Europe. The city is a major port and a hub for trade with Europe, and many European companies have operations in St. Petersburg. The city is also home to several prestigious universities and research institutions that have close collaborations with European academic institutions.
In conclusion, the perception and identity of St. Petersburg as a European city with a unique blend of Eastern and Western influences is a complex and multifaceted issue. This perception is shaped by a combination of historical, cultural, geographical, economic, and political factors that contribute to the city’s distinct character.
Table: Key Insights
| Key Insight | Explanation |
|---|---|
| St. Petersburg’s historical and cultural ties to Europe have shaped its European identity. | The city was founded as a “window to Europe” and has been influenced by European culture and ideas throughout its history. |
| St. Petersburg’s geographical location on the eastern edge of Europe has allowed it to absorb influences from both European and Asian cultures. | This unique location has contributed to the city’s rich and diverse cultural heritage. |
| St. Petersburg’s strong economic and political ties to Europe reinforce its European identity. | The city is a major port, a hub for trade with Europe, and home to several prestigious universities and research institutions with close collaborations with European counterparts. |
FAQs on “Is St. Petersburg, Russia in Europe?”
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions surrounding the geographical and cultural identity of St. Petersburg, Russia.
Question 1: Is St. Petersburg located in Europe or Asia?
Answer: Geographically, St. Petersburg lies on the eastern edge of Europe, near the border with Asia. Its unique location has historically positioned the city as a bridge between the two continents.
Question 2: Why is St. Petersburg considered a European city?
Answer: St. Petersburg’s historical and cultural ties to Europe are extensive. Founded by Peter the Great as a “window to Europe,” the city adopted European architectural styles, art, and urban planning. Additionally, St. Petersburg has strong economic and political connections with European countries.
Question 3: What are some of the European influences evident in St. Petersburg?
Answer: St. Petersburg’s European influences are visible in its architecture, with landmarks like the Winter Palace showcasing Baroque and Neoclassical styles. The city’s art scene has also been shaped by European movements, and its museums house vast collections of European masterpieces.
Question 4: Despite its European influences, does St. Petersburg have any Asian influences as well?
Answer: While St. Petersburg’s European influences are more prominent, the city’s location near the border with Asia has resulted in some cultural exchange. This is evident in certain architectural elements, such as onion domes and colorful facades, which reflect Russian Orthodox traditions.
Question 5: Is St. Petersburg politically affiliated with Europe?
Answer: St. Petersburg is part of the Russian Federation, which spans both Europe and Asia. As such, the city is subject to Russian laws and regulations and is represented by Russian diplomats internationally.
Question 6: How does St. Petersburg’s unique location influence its identity?
Answer: St. Petersburg’s position as a bridge between Europe and Asia has fostered a unique blend of Eastern and Western influences. The city’s architecture, culture, and economy all reflect this blend, creating a vibrant and cosmopolitan urban environment.
Summary: St. Petersburg’s geographical location, historical ties, and cultural influences have shaped its identity as a European city with a unique blend of Eastern and Western elements. Despite its political affiliation with Russia, the city maintains strong connections with Europe and plays an important role in cultural and economic exchanges between the two continents.
Transition: To further explore the historical, cultural, and geographical factors that contribute to St. Petersburg’s unique identity, continue reading the main article.
Tips to Understand the European Identity of St. Petersburg, Russia
Understanding the unique geographical and cultural identity of St. Petersburg requires a comprehensive approach. Here are several tips to delve deeper into this topic:
Tip 1: Examine Historical Context
St. Petersburg’s founding in 1703 as a “window to Europe” by Peter the Great was a pivotal moment in shaping its European orientation. Explore the city’s history to understand how this decision influenced its architecture, culture, and political ties.
Tip 2: Analyze Architectural Influences
St. Petersburg’s architectural heritage showcases a blend of European styles, such as Baroque and Neoclassical, with traditional Russian elements. Examine buildings like the Winter Palace and Kazan Cathedral to identify these influences and understand their significance.
Tip 3: Consider Cultural Exchanges
The city has been a hub for cultural exchange between Russia and Europe. Visit museums like the Hermitage and attend cultural events to appreciate the diverse artistic and intellectual influences that have shaped St. Petersburg’s cultural landscape.
Tip 4: Explore Economic Connections
St. Petersburg’s economy is closely linked to European markets. Analyze the city’s trade relations, investments, and business ties with European countries to understand its economic integration with Europe.
Tip 5: Examine Transportation Networks
St. Petersburg’s connectivity to Europe is facilitated by major highways and railways. Explore these transportation networks and their impact on the movement of goods, people, and ideas between the city and other European destinations.
Summary: By employing these tips, you can gain a deeper understanding of the historical, cultural, and economic factors that contribute to St. Petersburg’s unique identity as a European city with deep connections to both East and West.
Transition: Continue reading the main article to explore these aspects of St. Petersburg’s identity in greater detail.
Conclusion
The exploration of “is st petersburg russia in europe” reveals a multifaceted identity shaped by a unique blend of geographical, historical, and cultural factors. St. Petersburg’s founding as a “window to Europe” and its enduring ties to European art, architecture, and politics firmly establish its European identity.
Despite its location on the eastern edge of Europe, St. Petersburg has consistently played a pivotal role in cultural and economic exchanges between East and West. The city’s vibrant cultural scene, cosmopolitan atmosphere, and strong connections to European markets and institutions further reinforce its European orientation.
Recognizing St. Petersburg’s unique position as a bridge between Europe and Asia is crucial for understanding its past, present, and future. As the city continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly maintain its distinct blend of Eastern and Western influences, serving as a testament to the interconnectedness of our world.