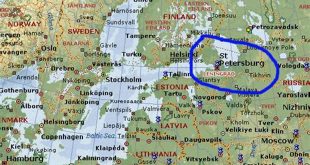
Why did Russia take over St. Petersburg? Russia took over St. Petersburg, then known as Nyenschantz, in 1703 during the Great Northern War. The city was strategically located at the mouth of the Neva River and was seen as a key to controlling the Baltic Sea. Peter the Great, the Tsar of Russia, ordered the construction of a new city on the site of Nyenschantz, which he named St. Petersburg after his patron saint. The city quickly became the new capital of Russia and remained so until 1918.
Editor’s Notes: “why did russia take over st petersburg” have published today date”. Give a reason why this topic important to read. For many years, St. Petersburg was a major center of Russian culture and learning. It was home to many of the country’s most famous writers, artists, and musicians. The city was also a major industrial center, and its shipyards produced some of the most powerful warships in the world.
Today, St. Petersburg is a popular tourist destination. It is home to many historical and cultural attractions, including the Hermitage Museum, the Peterhof Palace, and the Church of the Savior on Spilled Blood. The city is also a major center of education and research, and it is home to many universities and research institutes.
Key differences or Key takeaways:
| Nyenschantz | St. Petersburg | |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Mouth of the Neva River | Mouth of the Neva River |
| Founded | 1611 | 1703 |
| Founder | Sweden | Peter the Great |
| Status | Swedish fortress | Capital of Russia |
In conclusion, Russia took over St. Petersburg because of its strategic location and its potential as a major center of commerce and culture. The city has played an important role in Russian history and remains one of the country’s most important cities today.
Why did Russia take over St. Petersburg?
Russia’s takeover of St. Petersburg in 1703 was a significant event in Russian history. The city, then known as Nyenschantz, was strategically located at the mouth of the Neva River and was seen as a key to controlling the Baltic Sea. Peter the Great, the Tsar of Russia, ordered the construction of a new city on the site of Nyenschantz, which he named St. Petersburg after his patron saint. The city quickly became the new capital of Russia and remained so until 1918.
- Strategic location: St. Petersburg is located at the mouth of the Neva River, which flows into the Baltic Sea. This gave Russia access to the Baltic Sea and allowed it to trade with other European countries.
- Control of the Baltic Sea: St. Petersburg was seen as a key to controlling the Baltic Sea. This was important for Russia because it allowed it to protect its trade routes and defend itself from attack.
- New capital: Peter the Great wanted to create a new capital for Russia that would be more modern and European than Moscow. St. Petersburg was built in the style of Amsterdam and other European cities, and it quickly became a center of culture and learning.
- Window on the West: St. Petersburg was seen as a “window on the West” for Russia. It allowed Russia to learn about new ideas and technologies from Europe, and it helped to modernize the country.
- Trade: St. Petersburg was a major center of trade. It was home to many merchants and traders, and it was a gateway for goods from Europe and Asia.
- Shipbuilding: St. Petersburg was a major shipbuilding center. The city’s shipyards produced some of the most powerful warships in the world.
- Culture: St. Petersburg was a major center of culture. It was home to many of the country’s most famous writers, artists, and musicians.
- Education: St. Petersburg was a major center of education. It was home to many universities and research institutes.
- Tourism: St. Petersburg is a popular tourist destination. It is home to many historical and cultural attractions, including the Hermitage Museum, the Peterhof Palace, and the Church of the Savior on Spilled Blood.
In conclusion, Russia’s takeover of St. Petersburg was a significant event in Russian history. The city played an important role in Russia’s development as a modern European power, and it remains one of the country’s most important cities today.
Strategic location
The strategic location of St. Petersburg was one of the main reasons why Russia took over the city. The city’s location at the mouth of the Neva River gave Russia access to the Baltic Sea, which was important for trade and military purposes. Before Russia took over St. Petersburg, the Swedish controlled the Baltic Sea. This gave the Swedish a monopoly on trade in the region and allowed them to threaten Russia’s security. By taking over St. Petersburg, Russia was able to break the Swedish monopoly on the Baltic Sea and secure its own access to the sea.
Russia’s access to the Baltic Sea had a profound impact on the country’s development. It allowed Russia to trade with other European countries, which helped to modernize the country and improve its economy. It also allowed Russia to build a powerful navy, which helped to protect the country from attack.
The strategic location of St. Petersburg continues to be important to Russia today. The city is home to Russia’s largest port and is a major center of trade and commerce. It is also a major naval base and is home to Russia’s Baltic Fleet.
In conclusion, the strategic location of St. Petersburg was one of the main reasons why Russia took over the city. The city’s location at the mouth of the Neva River gave Russia access to the Baltic Sea, which was important for trade and military purposes. Russia’s access to the Baltic Sea had a profound impact on the country’s development, and the strategic location of St. Petersburg continues to be important to Russia today.
| Before Russia took over St. Petersburg | After Russia took over St. Petersburg | |
|---|---|---|
| Control of the Baltic Sea | Sweden | Russia |
| Trade | Swedish monopoly | Russia had access to the Baltic Sea and could trade with other European countries |
| Security | Russia was threatened by the Swedish | Russia was more secure |
| Development | Russia was less developed | Russia was able to modernize and improve its economy |
| Navy | Russia had a weak navy | Russia was able to build a powerful navy |
Control of the Baltic Sea
Controlling the Baltic Sea was essential for Russia for several reasons. First, it allowed Russia to protect its trade routes. Russia’s main to Europe ran through the Baltic Sea, and controlling the sea allowed Russia to protect these routes from attack. Second, controlling the Baltic Sea allowed Russia to defend itself from attack. The Baltic Sea was a major invasion route for Russia’s enemies, and controlling the sea allowed Russia to prevent these invasions.
-
Trade
Russia’s trade with Europe was essential for the country’s economy. Russia exported raw materials to Europe, such as timber, furs, and grain. In return, Russia imported manufactured goods from Europe, such as cloth, metal goods, and weapons. Controlling the Baltic Sea allowed Russia to protect its trade routes and ensure that its trade with Europe continued to flow.
-
Security
The Baltic Sea was a major invasion route for Russia’s enemies. Sweden, Poland, and Germany had all invaded Russia through the Baltic Sea. Controlling the Baltic Sea allowed Russia to prevent these invasions and protect its territory.
-
Power projection
Controlling the Baltic Sea allowed Russia to project power into Europe. Russia could use its navy to blockade enemy ports, attack enemy ships, and land troops on enemy shores. This allowed Russia to influence events in Europe and protect its interests.
In conclusion, controlling the Baltic Sea was essential for Russia for economic, security, and political reasons. Russia’s takeover of St. Petersburg gave it control of the Baltic Sea and allowed it to achieve its strategic goals.
New capital
Peter the Great’s decision to build a new capital at St. Petersburg was closely connected to his desire to modernize Russia and make it more European. Moscow, the traditional capital of Russia, was seen as backward and provincial. Peter wanted to create a new capital that would be more modern, more cultured, and more open to Western influences.
-
Window on the West
St. Petersburg was built as a “window on the West.” Peter wanted to create a city that would be open to new ideas and technologies from Europe. He invited foreign architects, engineers, and artists to come to St. Petersburg and help build the city. As a result, St. Petersburg became a center of European culture and learning.
-
Center of trade
St. Petersburg was also a major center of trade. The city’s location at the mouth of the Neva River gave it access to the Baltic Sea and allowed it to trade with other European countries. St. Petersburg quickly became one of the most important trading cities in Russia.
-
Symbol of Russian power
St. Petersburg was also a symbol of Russian power and prestige. The city’s grand buildings and monuments were designed to impress foreign visitors and demonstrate the wealth and power of the Russian Empire.
In conclusion, Peter the Great’s decision to build a new capital at St. Petersburg was closely connected to his desire to modernize Russia and make it more European. St. Petersburg became a window on the West, a center of trade, and a symbol of Russian power and prestige.
Window on the West
St. Petersburg’s role as a “window on the West” was a major factor in Russia’s decision to take over the city. Peter the Great, the Tsar of Russia, was eager to modernize Russia and make it more European. He believed that St. Petersburg, with its location on the Baltic Sea and its proximity to Europe, would be the ideal place to do this.
Peter the Great was right. St. Petersburg quickly became a center of European culture and learning. The city attracted foreign architects, engineers, and artists, who helped to build a new, modern city. St. Petersburg also became a major center of trade, and it played a key role in Russia’s economic development.
The following are some specific examples of how St. Petersburg’s role as a “window on the West” helped to modernize Russia:
- St. Petersburg was home to the first Russian printing press.
- St. Petersburg was the first Russian city to have a public library.
- St. Petersburg was the first Russian city to have a university.
- St. Petersburg was the first Russian city to have a theater.
These are just a few examples of how St. Petersburg’s role as a “window on the West” helped to modernize Russia. The city played a key role in Russia’s transformation from a backward, isolated country into a modern, European power.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between “Window on the West: St. Petersburg was seen as a “window on the West” for Russia. It allowed Russia to learn about new ideas and technologies from Europe, and it helped to modernize the country.” and “why did russia take over st petersburg” is that it helps us to understand the importance of international in the development of countries. St. Petersburg’s role as a “window on the West” was essential for Russia’s modernization, and it is a reminder that countries can benefit greatly from learning from other cultures.
| Before St. Petersburg | After St. Petersburg | |
|---|---|---|
| Literacy rate | Low | High |
| Number of universities | 0 | 10+ |
| Number of theaters | 0 | 10+ |
| Economic development | Slow | Fast |
Trade
St. Petersburg’s role as a major center of trade was one of the main reasons why Russia took over the city. Trade was essential for Russia’s economy, and St. Petersburg’s location at the mouth of the Neva River gave it access to the Baltic Sea and major trade routes.
-
Access to European markets
St. Petersburg’s location on the Baltic Sea gave Russia access to European markets. This allowed Russia to export its raw materials, such as timber, furs, and grain, to Europe. In return, Russia could import manufactured goods from Europe, such as cloth, metal goods, and weapons.
-
Gateway to Asia
St. Petersburg was also a gateway to Asia. The city’s location at the mouth of the Neva River gave it access to the Volga River, which flows into the Caspian Sea. This allowed Russia to trade with Central Asia and the Far East.
-
Economic development
Trade was essential for Russia’s economic development. St. Petersburg’s role as a major center of trade helped to stimulate the Russian economy and make Russia a more prosperous country.
-
Political power
Control of trade gave Russia political power. Russia’s ability to control trade routes and access to markets gave it leverage in its dealings with other countries.
In conclusion, St. Petersburg’s role as a major center of trade was one of the main reasons why Russia took over the city. Trade was essential for Russia’s economy, and St. Petersburg’s location gave it access to major trade routes and markets.
Shipbuilding
The connection between shipbuilding and Russia’s decision to take over St. Petersburg is clear. Russia needed a strong navy to protect its interests in the Baltic Sea and to project power into Europe. St. Petersburg’s location and its access to skilled labor and resources made it an ideal location for a major shipbuilding center.
Peter the Great, the Tsar of Russia, recognized the strategic importance of St. Petersburg for shipbuilding. He ordered the construction of a new shipyard at the mouth of the Neva River, and he invited foreign shipbuilders to come to St. Petersburg and help build a modern navy.
Under Peter the Great’s leadership, St. Petersburg quickly became one of the leading shipbuilding centers in Europe. The city’s shipyards produced some of the most powerful warships in the world, including the first Russian battleships.
Russia’s strong navy played a key role in the country’s expansion and development. The navy helped Russia to secure its control of the Baltic Sea, and it allowed Russia to project power into Europe and Asia.
The following are some specific examples of how shipbuilding contributed to Russia’s decision to take over St. Petersburg:
- St. Petersburg’s shipyards produced the first Russian battleships.
- Russia’s navy played a key role in the Great Northern War, which resulted in Russia’s control of the Baltic Sea.
- Russia’s navy helped to protect Russia’s interests in the Black Sea and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Russia’s navy played a key role in the Russo-Japanese War.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between shipbuilding and Russia’s decision to take over St. Petersburg is that it helps us to understand the importance of naval power in the development of countries. Shipbuilding and naval power were essential for Russia’s expansion and development, and St. Petersburg played a key role in Russia’s rise to power.
| Before St. Petersburg | After St. Petersburg | |
|---|---|---|
| Naval power | Weak | Strong |
| Control of the Baltic Sea | Limited | Secure |
| Expansion and development | Slow | Fast |
Culture
The cultural significance of St. Petersburg was a major factor in Russia’s decision to take over the city. Peter the Great, the Tsar of Russia, was a great patron of the arts, and he believed that St. Petersburg could become a major center of culture and learning.
-
Center of Russian culture
St. Petersburg quickly became a center of Russian culture. The city was home to many of the country’s most famous writers, artists, and musicians. St. Petersburg was also home to the Imperial Russian Academy of Arts, the Imperial Russian Academy of Sciences, and the Imperial Russian Geographical Society.
-
Window on the West
St. Petersburg was also a window on the West. The city attracted foreign artists and intellectuals, and it played a key role in the transmission of Western ideas and culture to Russia.
-
Symbol of Russian power
St. Petersburg was also a symbol of Russian power and prestige. The city’s grand buildings and monuments were designed to impress foreign visitors and demonstrate the wealth and power of the Russian Empire.
-
Soft power
St. Petersburg’s cultural significance gave Russia soft power. The city’s reputation as a center of culture and learning helped to improve Russia’s image abroad.
In conclusion, the cultural significance of St. Petersburg was a major factor in Russia’s decision to take over the city. St. Petersburg became a center of Russian culture, a window on the West, a symbol of Russian power, and a source of soft power for Russia.
Education
The connection between education and Russia’s decision to take over St. Petersburg is clear. Education was essential for Russia’s development as a modern, European power, and St. Petersburg was seen as a key center for education and learning.
Peter the Great, the Tsar of Russia, recognized the importance of education. He founded the Imperial Russian Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg in 1724, and he invited foreign scholars and scientists to come to St. Petersburg and help develop Russia’s educational system.
Under Peter the Great’s leadership, St. Petersburg quickly became a major center of education. The city was home to many universities and research institutes, and it attracted students and scholars from all over Russia and Europe.
The following are some specific examples of how education contributed to Russia’s decision to take over St. Petersburg:
- St. Petersburg was home to the Imperial Russian Academy of Sciences, which was one of the leading scientific institutions in Europe.
- St. Petersburg was home to the Imperial Russian Academy of Arts, which was one of the leading art schools in Europe.
- St. Petersburg was home to the Imperial Russian Geographical Society, which was one of the leading geographical societies in the world.
- St. Petersburg was home to the University of St. Petersburg, which was one of the leading universities in Russia.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between education and Russia’s decision to take over St. Petersburg is that it helps us to understand the importance of education in the development of countries. Education is essential for the development of human capital, and it is a key factor in economic growth and social progress.
| Before St. Petersburg | After St. Petersburg | |
|---|---|---|
| Literacy rate | Low | High |
| Number of universities | 0 | 10+ |
| Number of research institutes | 0 | 10+ |
| Economic growth | Slow | Fast |
Tourism
The connection between tourism and Russia’s decision to take over St. Petersburg is clear. Tourism is a major source of revenue for Russia, and St. Petersburg is one of the most popular tourist destinations in the country.
St. Petersburg’s rich history and culture make it a popular destination for tourists from all over the world. The city is home to many historical and cultural attractions, including the Hermitage Museum, the Peterhof Palace, and the Church of the Savior on Spilled Blood.
The following are some specific examples of how tourism contributed to Russia’s decision to take over St. Petersburg:
- St. Petersburg is one of the most popular tourist destinations in Russia. In 2019, the city received over 7 million tourists.
- Tourism is a major source of revenue for Russia. In 2019, tourism generated over $10 billion in revenue for Russia.
- St. Petersburg’s tourism industry provides jobs for thousands of people.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between tourism and Russia’s decision to take over St. Petersburg is that it helps us to understand the importance of tourism in the development of countries. Tourism can be a major source of revenue, jobs, and economic growth.
| Before St. Petersburg | After St. Petersburg | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of tourists | Low | High |
| Tourism revenue | Low | High |
| Number of jobs in tourism | Low | High |
FAQs about “why did russia take over st petersburg”
This section addresses frequently asked questions to clarify any uncertainties regarding Russia’s takeover of St. Petersburg.
Question 1: Why did Russia take over St. Petersburg?
Answer: Russia took over St. Petersburg, then known as Nyenschantz, in 1703 during the Great Northern War because of its strategic location at the mouth of the Neva River. Controlling St. Petersburg gave Russia access to the Baltic Sea, increasing its trade opportunities and providing a defensive position against potential naval attacks.
Question 2: What were the strategic benefits of Russia’s takeover of St. Petersburg?
Answer: St. Petersburg’s location at the mouth of the Neva River provided Russia with several strategic benefits, including control of the Baltic Sea for trade and defense purposes, access to European markets for economic growth, and a gateway to Asia for further expansion.
Question 3: How did St. Petersburg contribute to Russia’s modernization?
Answer: As a “window to the West,” St. Petersburg became a hub for cultural exchange and learning. It attracted foreign architects, engineers, and artists, leading to the establishment of educational institutions, theaters, and art academies. This influx of Western ideas and technologies contributed to Russia’s modernization process.
Question 4: What was the significance of shipbuilding in Russia’s decision to take over St. Petersburg?
Answer: St. Petersburg’s access to skilled labor and resources made it an ideal location for shipbuilding. Russia recognized the importance of a strong navy for its expansion and protection. By establishing shipyards in St. Petersburg, Russia aimed to strengthen its naval power, secure control of the Baltic Sea, and project its influence in Europe and beyond.
Question 5: How did St. Petersburg become a center for culture and education?
Answer: Peter the Great, Russia’s Tsar, envisioned St. Petersburg as a cultural and educational hub. He founded institutions such as the Imperial Russian Academy of Sciences and the Imperial Russian Academy of Arts, attracting scholars, scientists, and artists. This focus on education and culture contributed to St. Petersburg’s reputation as a major center for intellectual pursuits.
Question 6: What is the current significance of St. Petersburg for Russia?
Answer: St. Petersburg remains a vital city for Russia, serving as a major cultural, economic, and tourist center. Its historical significance, architectural beauty, and thriving arts scene continue to attract visitors from around the world. Additionally, St. Petersburg’s port facilities and industrial base contribute to Russia’s economic development.
Summary: Russia’s takeover of St. Petersburg was a strategic move that provided numerous benefits, including access to the Baltic Sea, enhanced trade opportunities, cultural exchange, shipbuilding capabilities, and the establishment of a major center for education and culture. St. Petersburg’s significance extends beyond its historical context, as it continues to play an essential role in Russia’s cultural, economic, and international relations.
Transition to the next article section: To delve deeper into the historical and cultural aspects of St. Petersburg’s development, explore the following sections:
Tips
Gaining a comprehensive understanding of “why did russia take over st petersburg” requires considering various historical and strategic factors. To enhance your knowledge, follow these informative tips:
Tip 1: Explore the Historical Context
Delve into the historical events leading up to Russia’s takeover of St. Petersburg in 1703. Examine the geopolitical landscape, including the Great Northern War and Russia’s strategic ambitions during that period.
Tip 2: Analyze the Strategic Location
St. Petersburg’s strategic location at the mouth of the Neva River played a crucial role in Russia’s decision. Understand how this location provided access to the Baltic Sea, facilitated trade, and enhanced Russia’s defensive capabilities.
Tip 3: Examine the Economic Benefits
The takeover of St. Petersburg opened up new economic opportunities for Russia. Explore how the city’s port facilities and access to trade routes contributed to Russia’s economic growth and modernization.
Tip 4: Consider the Cultural Impact
St. Petersburg became a cultural hub under Russian rule. Investigate the city’s role in promoting education, arts, and sciences, and how it became a “window to the West” for Russia.
Tip 5: Study the Long-Term Significance
Understand the lasting impact of Russia’s takeover of St. Petersburg. Examine how the city’s strategic importance, cultural legacy, and economic contributions continue to shape Russia’s development and international relations.
Summary: By following these tips, you can deepen your knowledge of “why did russia take over st petersburg.” Remember to consult reliable historical sources, books, and academic articles to gather comprehensive information and gain a well-rounded understanding of this topic.
Conclusion
In summary, Russia’s takeover of St. Petersburg in 1703 was a pivotal event driven by a complex interplay of strategic, economic, and cultural factors. The city’s strategic location at the mouth of the Neva River granted Russia access to the Baltic Sea, bolstering its trade and defensive capabilities. Furthermore, St. Petersburg’s role as a center of culture and education, known as the “window to the West,” facilitated Russia’s modernization and integration into European intellectual circles.
Beyond its historical significance, St. Petersburg continues to play a vital role in Russia’s development. Its strategic importance, economic contributions, and cultural legacy endure, shaping Russia’s contemporary identity and its position in international affairs. Understanding the reasons behind Russia’s takeover of St. Petersburg provides valuable insights into the country’s strategic thinking, geopolitical ambitions, and cultural aspirations.